As a Manager, it is crucial to be able identify risks in your project as early as possible to be able to highlight the risk and mitigate the risk timely to avoid any serious consequences. There are many ways you can assess and monitor risks depending upon your type of project and type of your responsibility. However, articulating and communicating risks are equally important as assessing risks.
1. Proactive Risk Identification with Agile Practices:
In Agile or Scrum based projects , most of the risks can be identified if we follow Agile/Scrum best practices like following. As a Manager,
- Continuous Advance grooming of features/User Stories.
- Prioritization: Use Agile principles to prioritize risks based on their impact and likelihood, addressing the most critical ones first
- Iterative Feedback: Seek feedback from stakeholders and end-users regularly to detect potential risks related to requirements, expectations, or market changes.
- Sprint Planning: Include risk assessment as part of sprint planning, considering potential impediments and dependencies.
- Sprint Retro: Get feedback from the team on what went wrong and create corrective action items.
- Using Risk Burndown Chart: Make note of risks and track them using burndown chart.
2. Use of Risk Analysis Techniques:
1. SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify and evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats involved in a project, business venture, or organization. It provides a structured framework for assessing both internal factors (strengths and weaknesses) and external factors (opportunities and threats), enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning.
How to do SWOT Analysis:
Create a grid divided into four quadrants (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to visually organize and analyze the identified factors. To perform the SWOT , you simply need to put your points in each of the four quadrants/boxes .
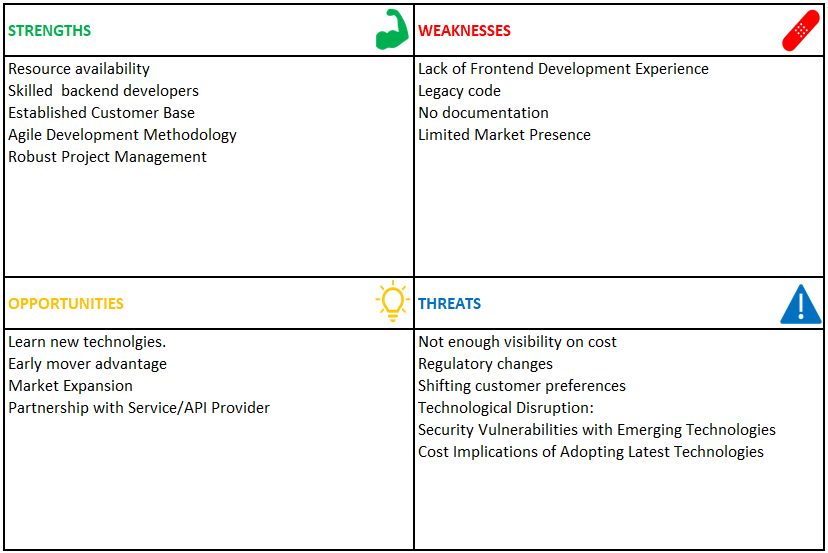
Strengths:What are the strengths you have in executing this project. These could include skills, resources, technology, market position, reputation, or unique capabilities.
Weaknesses: These could be internal factors that place an organization at a disadvantage relative to others. These could include gaps in skills, lack of resources, outdated technology, poor reputation, or inefficiencies.
Opportunities: These are external factors that the organization could potentially exploit to its advantage. These could include market trends, new technologies, changes in regulations, emerging markets, or unmet customer needs.
Threats: These are also external factors that could pose a risk to the organization’s performance or viability. These could include competitive pressures, economic downturns, regulatory changes, technological advancements by competitors, or shifting consumer preferences.
Tools: SWOT Matrix (4-Quadrant Grid): You can simply use an excel with four boxes to note down SWOT and perform SWOT analysis. Other useful tools are Draw.io, MIRO etc. You can also directly prepare in the Powerpoint/Keynotes if you need to present the same to the stakeholders.
2. Using Risk Assessment Models
Risk assessment models provide a structured approach to identifying and categorizing potential risks that could impact a project, organization, or process. By systematical examination these models ensure that no critical risk is overlooked.
Some of common risk assessment models are :
i)Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
FMEA is a systematic method for identifying potential failure modes in a design, process, or system, assessing their effects on system performance, and prioritizing them for mitigation.
Usage:
Suppose you are developing a new mobile banking application for a financial institution. The app will allow customers to perform various banking transactions securely on their smartphones.
To calculate Risk
Calculate Risk Priority Number (RPN)
RPN=Severity(S)×Occurrence(O)×Detection(D)
a. To calculate Risks Number, first identify Potential Failure Modes.
e.g of Failure Modes
- User unable to log in to the mobile banking app.
- App crashes when processing a large volume of transactions simultaneous
- User data compromised due to a security breach.
b. Second,assess severity (S):- 1- Low, 2 medium, 3 high, 5 critical
c. Third, assess Occurrence- Occassionally(1), intermittently(2), frequently(5)
d. Fourth assess Detection- issues detect at user level (4), using app logs (3), internally 2
Calculate RPN by multiplying the score for each Failure Modes. Higher the RPN, higher the risk.
RPN=Severity(S)×Occurrence(O)×Detection(D)
e.g= 2*3*4=24
Create Mitigation actions for each failure modes and monitor them regularly
ii) Risk Matrix
A risk matrix is a graphical representation used in risk assessment and risk management to evaluate the likelihood of an event occurring against its consequences. It helps in prioritizing risks based on their severity and likelihood, guiding decision-making regarding risk mitigation strategies.
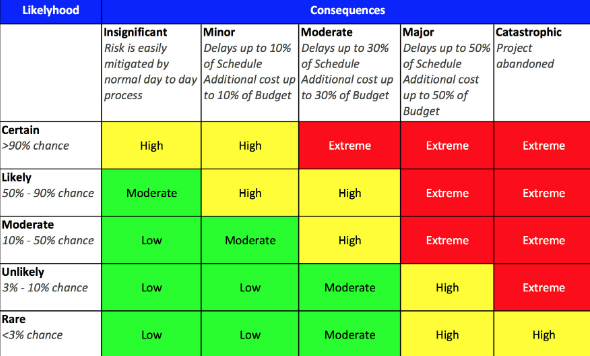
Place each identified risk on the risk matrix according to its assessed likelihood and consequences.
Prioritize risks based on their risk rating. High-risk events (e.g., High likelihood and High consequences) typically require immediate attention and mitigation.
Develop and implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies and controls based on the prioritized risks.